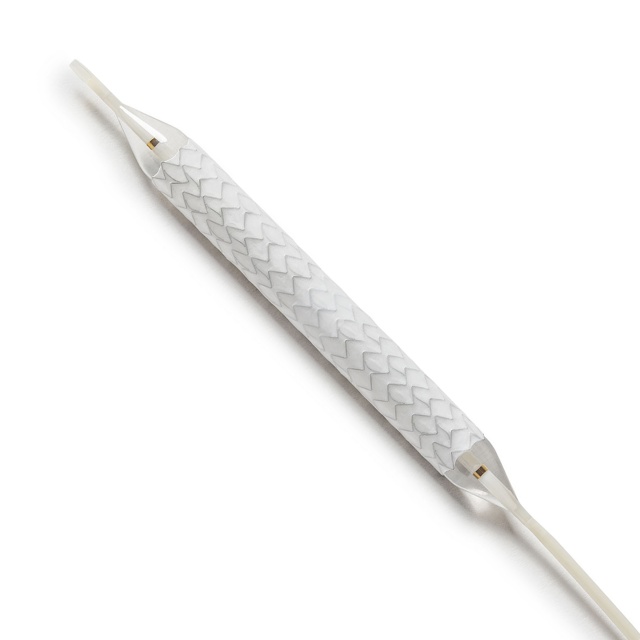
iCast covered stent system
iCast covered stents have the first to market balloon expandable, fully encapsulated stent design that has served physicians with more than 850,000 units sold. Known for its precision and predictability — the versatile iCast covered stent has been meeting the needs of surgeons and patients for 20 years, and is the only durable solution backed by decades of real-world evidence. [2][3]
Indication:
The iCast covered stent system is indicated for improving luminal diameter in patients with symptomatic atherosclerotic disease of the native common and/or external iliac arteries up to 110 mm in length, with a reference vessel diameter of 5 to 10 mm.
The iCast covered stent system is not available outside of the United States.
Bilateral common iliac restenosis remodeled with the iCast covered stent system
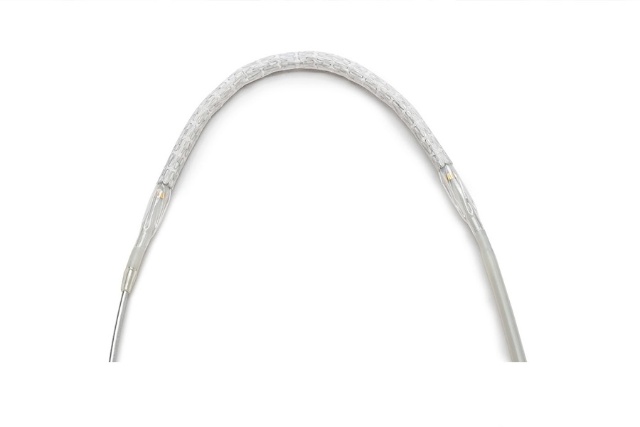

Predictable and Precise[2]
- Low profile, reliable stent retention force and secure trackability facilitate stent implantation[2]
- Designed for secure delivery and placement: average stent securement force is 2-4 times higher than peak insertion forces[2]
- 6 and 7 French compatible[2]
- Radiopaque markers enhance visibility during deployment and assist with accurate stent placement.[1]
- Designed for pushability and trackability through tortuous anatomy with conformance to iliac arteries [1]
- Predictable recoil and foreshortening promotes precise deployment [2]
Please see the iCast order information found in the documents tab for detailed compatibility.
Refer to Instructions for Use for current indications, warnings, contraindications, and precautions.
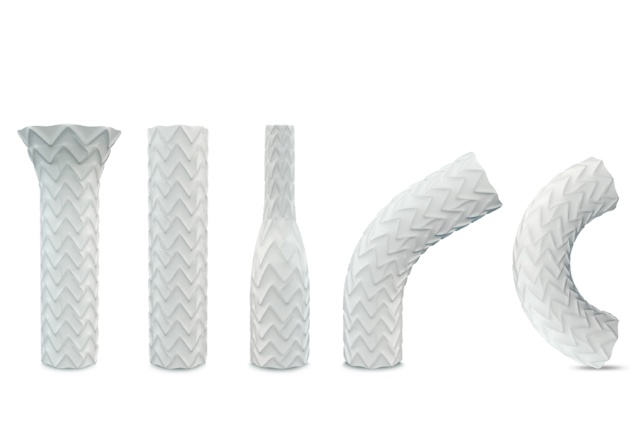

Versatile and Flexible[2]
- Full encapsulation with ePTFE helps mitigate the risks related to vessel perforation. [6] [9]
- Smooth inner lumen offers ease of navigation during re-intervention. [2]
- Able to post-dilate and flare stent: conforming to the anatomy and customizing each patient's treatment [1][8]
- 316L stainless steel struts provide additional radial force - designed to support stent patency.[1]
- Dog-bone inflation design is intended to reduce the chances of embolization [7]
- Stent structure, cell design, and system provide versatility and flexibility in delivery and placement.[2]
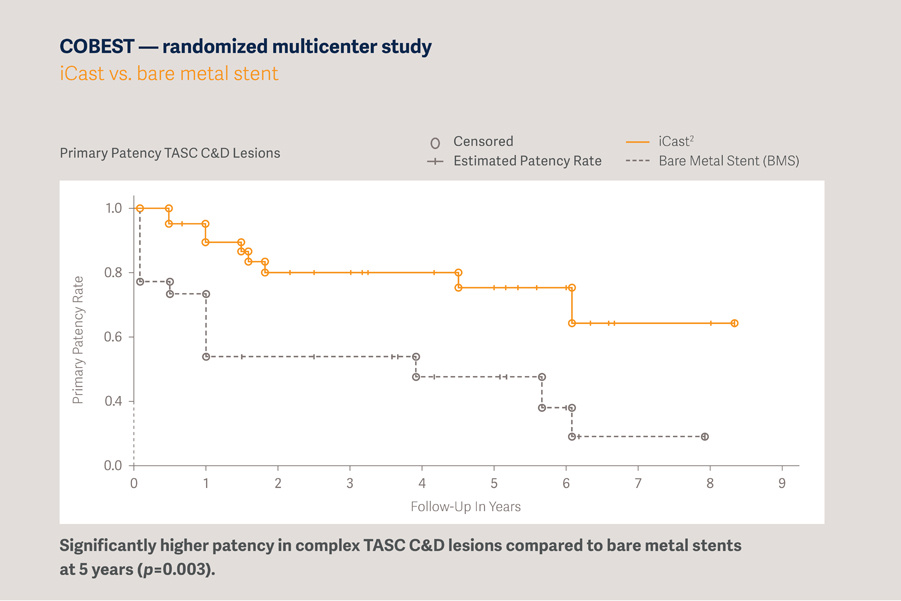
COBEST - 5 year results: iCast vs. Bare Metal Stent [1]
Systematic review of covered balloon-expandable stents for treating aortoiliac occlusive disease [3]
-
The iCast/Advanta V12 balloon-expandable covered stent has long-term, real-world follow-up, including a reported 5-year primary patency rate of 74.7%.
-
The iCast/Advanta V12 was the most common device studied in the literature from 2000-2019 (10/15 publications; 66.7%).
-
The iCast/Advanta V12 studies treated patients with more severe disease (a greater number of TASC C&D lesions) and more severe symptoms (more Rutherford classification 4 & 5) compared to patients enrolled in clinical trials studying other covered balloon-expandable stents.
-
Freedom from TLR: Results were comparable for all covered balloon-expandable stents at 1 year. The iCast/Advanta V12 has long-term target lesion revascularization data.
iCARUS: Single-Arm IDE study with 3-year follow-up[4]
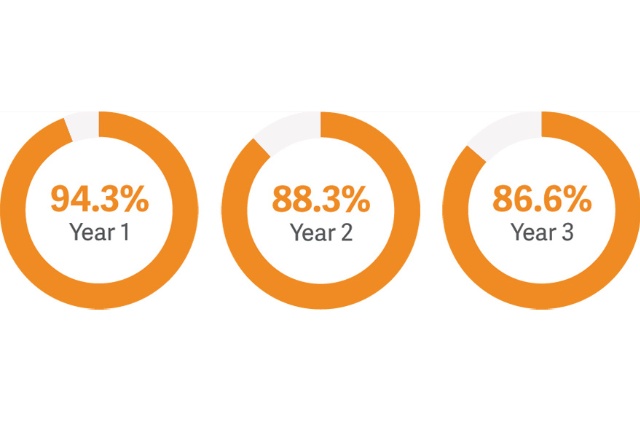
Freedom from Target Lesion Revascularization (TLR)
- Real-world patient population with multiple lesions and bilateral disease
- Study showed sustained clinical benefit with freedom from target lesion revascularization (TLR) up to 3 years
Pre and post images from occlusive disease treatment with iCast covered stent system
Bilateral illiac artery occlusion
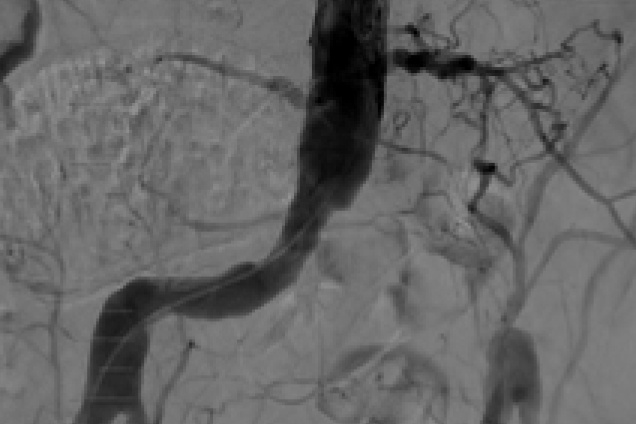
Pre treatment
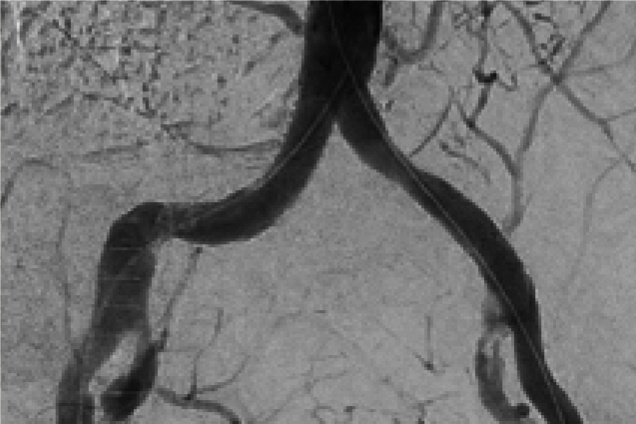
Post treatment
Restoration of the lumen diameter with iCast covered stent in RIA. iCast covered stents overlapped in LIA.
RIA: Right iliac artery
LIA: Left iliac artery
Bilateral common iliac artery occlusion
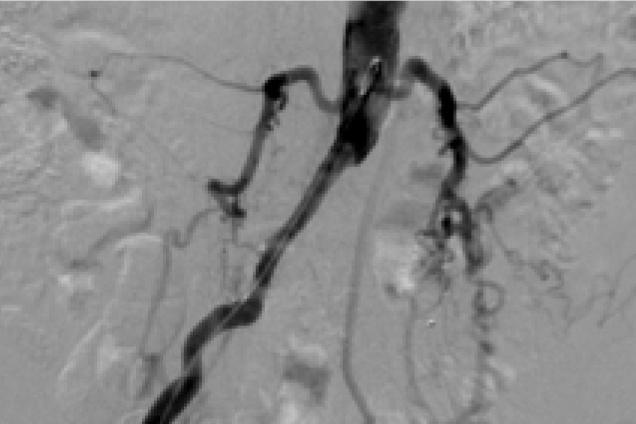
Pre treatment
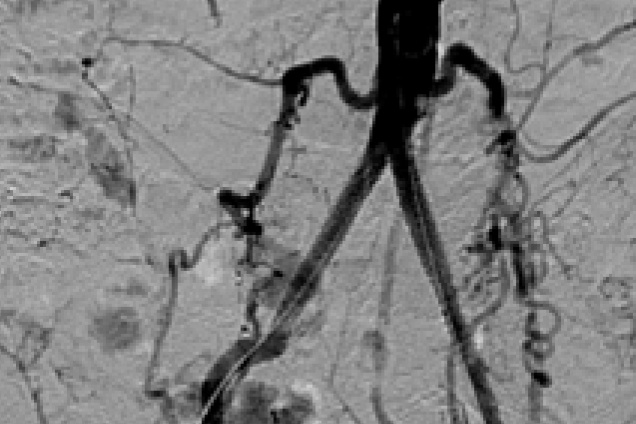
Post treatment
Restoration of the lumen diameter with iCast covered stents in RIA and LIA.
RIA: Right iliac artery
LIA: Left iliac artery
Marketing Sales - Data Sheet
-
iCast Datasheet